-
Xingming Road, Yanyuan, Xingtan, Shunde, Foshan, Guangdong
A Compulsory Course on Tires from Specifications to Classification
Abstract
As the only medium for vehicles to contact the ground, the performance of tires is directly related to driving safety, fuel economy and driving experience. This article systematically sorts out the core knowledge of tires by interpreting the meaning of tire models, analyzing mainstream classification standards, disassembling specification parameter codes, and combining data from authoritative institutions. The article focuses on analyzing 8 key dimensions: specification parameters, structural differences, speed ratings, production date identification, special symbol meanings, wear warning mechanisms, purchase matching principles and maintenance points, providing car owners with a scientific tire selection guide.
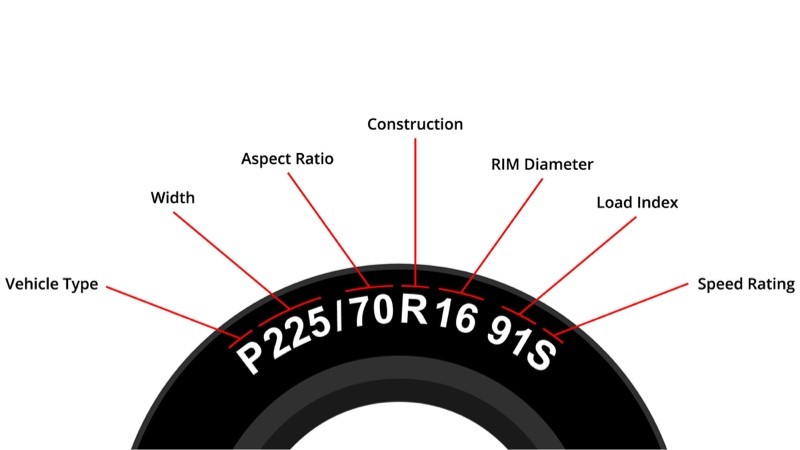
I. Tire specifications: the security code behind the numbers and letters
The internationally accepted tire specification marking method (such as 215/70R15) includes 4 core parameters: tire width 215mm, aspect ratio 70%, radial structure (R), and rim diameter 15 inches. A study by the US Department of Transportation pointed out that a tire width error of ±3% will increase the braking distance by 5.8% (NHTSA, 2020). The aspect ratio directly affects the balance between handling and comfort. BMW’s technical white paper recommends that luxury models use tires with an aspect ratio of <60% (BMW Group, 2022). Special markings such as 6.00-12 represent bias tires, whose lateral stiffness is 40% lower than that of radial tires (Michelin technical report).
Second, structural revolution: the century showdown between radial and bias tires
Radial tires (Radial) use radial ply design, which reduces rolling resistance by 20% compared to bias tires (Bridgestone laboratory data). Statistics from the Federal Highway Administration of the United States show that the popularity of radial tires has reduced the tire blowout rate of trucks by 63% (FHWA, 2019). Bias tires are still retained in special areas, such as agricultural tractors due to their puncture resistance, but it should be noted that the maximum speed should not exceed 80km/h (John Deere Equipment Manual).
3. Speed rating: Hidden speed warning light
The speed rating letter corresponds to the maximum safe speed. For example, V (240km/h) requires the tire body to use aramid fiber reinforcement. Porsche tests show that the risk of tire temperature rising to the critical point increases by 7 times when the speed exceeds the limit by 20% (Porsche Engineering, 2021). The EU tire labeling law requires the speed rating to be marked. Consumers can check the certification information through the ETRMA official website.
4. Production date: rubber time memory
The last four digits of the DOT code 1805 indicate that it was produced in the 18th week of 2005. The rubber aging curve shows that the performance decays by 40% in 6 years (German ADAC test). The American Rubber Manufacturers Association recommends that tires that have been used for more than 7 years must be replaced even if the tread depth meets the standard (RMA, 2022). The inspection guide can be obtained through the NHTSA tire aging special page.
V. Special symbols: Genetic map of environmental adaptation
The M+S (mud and snow) logo must be combined with a 3D snowflake icon to meet the severe winter standard (Transport Canada specification). The braking distance of the three-peak snowflake certified tire on ice is shortened by 34% (Nokia tire winter test). When the tread depth is less than 3mm on rainy days, the wet grip is reduced by 45% (Continental Group research report).
VI. Wear indicator: The life scale of the tire
The legal wear limit is 1.6mm, but the FIA test shows that when the tread is less than 3mm, the 60km/h wet braking distance increases by 8.2 meters. When the Michelin human logo is worn to 1.6mm, the tire drainage efficiency is only 23% of that of a new tire (Michelin Technology White Paper). It is recommended to use a tread depth gauge for monthly testing.
Seventh, purchase rules: the golden triangle of precise matching
Follow the “3C principle”: climate, load (Cargo), control (Control). The European tire labeling system provides purchase references from three dimensions: fuel efficiency (A-G grade), wet grip (A-E grade), and noise (dB value). For details, please refer to the graphical standard interpretation [ETRTO Guide] (https://www.etrto.org).
Eight, Maintenance Tips: Six Disciplines to Extend Life
- Tire pressure monitoring: monthly inspection, deviation > 10% accelerates wear
- Four-wheel alignment: correction every 20,000 kilometers to reduce uneven wear
- Dynamic balancing: must be redone after tire repair
- Replacement rules: cross replacement every 8,000 kilometers
- Storage specifications: avoid direct sunlight, store vertically
- Emergency treatment: do not remove nails, keep driving at low speed
Summary
From specification parameter decoding to structural characteristics analysis, from speed level recognition to maintenance system establishment, tire management is a systematic project. Data shows that standardized use of tires can reduce traffic accident rates by 31% and save an average of €180 in fuel costs per year (EU Traffic Committee report). It is recommended that car owners regularly visit professional platforms such as TyreSafe to obtain the latest technical trends, so that each tire can become a reliable safety guard.








